Today, structured cabling infrastructure has a much bigger role than it had in the past. Access to high-speed broadband connectivity, rapid growth in internet traffic, variety of bandwidth-intensive applications and need for connecting plethora of devices in Local Area Networks are driving the need for reliable structured cabling solution. High performance Data Centre networks and Local Area Networks (LANs) cannot perform well without appropriate structured cabling infrastructure.
Evolution of CAT 6A
LAN Technologies have evolved greatly over the years, and Ethernet has indigenized technology for LANs. Networks too needed to evolve rapidly to support the growing demand for application and technologies that are bandwidth hungry. For instance, Cat-5e was designed to support 100Mbps speed for 100 meter distance, while Cat 6 supported 1Gbps speed for 100 meter distance and also supported 10Gbps for reduced distance between 30* to 55mtr*. This is where Cat-6A comes in, as it supports speed for complete 100-meter length, making it highly relevant for modern day network need.
Thus, IEEE published a draft standard (Std 802.3an) in October 2004 and with this Cat 6A was born. Augmented CAT-6 or CAT-6A as it is referred to is capable of supporting data transfer rates of up to 10Gbps at a maximum bandwidth of 500MHz. CAT-6A has additional and tighter twists and designs to reduce cross talk. CAT-6A is also backwards compatible with CAT-6 and CAT-5e. However, speed performance will be limited to the lowest category cable or connector that is installed in the link. Unique proposition of CAT 6A cable is that it supports 10Gbps along with high power POE, thus making it highly suitable for new generation application.
| Category# | Bandwidth | Distance for 1G | Distance for 10G | Speed | Connector | Comments |
| CAT – 5E | 100 MHz | 100m | 1G,2.5G | RJ45 | ||
| CAT- 6 | 250 MHz | 100m | 37-55m* | 1G,2.5G,5G | RJ45 | Distance limitation for 10G |
| CAT-6A | 500 MHz | 100m | 100m | 1G,2.5G,5G and 10G | RJ45 | Better support Higher Power (POE++) |
| CAT-7 | 600 MHz | 100m | 100m | 1G,10G | Non-RJ45 | |
| CAT-7A | 1000 MHz | 100m | 100m | 1G,10G | Non-RJ45 | |
| CAT-8 | 2000 MHz | 100m | 100m | 1G,10G,25G,4G, 25/40G up to 30m) | Class I: RJ-45 Class II: Non-RJ45 | 30m channel and 2 connector channels |
| Note: *- Distance given only for reference to understand. Actual distance can very (can be less or same) depending on crosstalk, cable/connector quality, Installation, field environment etc. | ||||||
CAT-6 cabling provides many advantages compared to CAT-5e cabling infrastructure. CAT-6 supports higher bandwidth over CAT-5e and allows for higher data transfer rates. Therefore, CAT-6 has now become the minimum requirement for new cabling installations.
CAT-6A is an augmented category, that is becoming increasingly popular these days. Data Centres, hospitals and universities have adopted CAT-6A as a new minimum requirement. In comparison to Cat6, Cat- 6A has more robust design, which reduces alien crosstalk and improves the signal-to-noise ratio.
CAT-7 and CAT-7A are not widely adopted as they do not use standard Rj45 connector in channel.
CAT 8 was developed to support the IEEE 25GBASE-T and 40GBASE-T specs, CAT8 has a maximum channel length of 30 meters with two connectors and is tested from 1 MHz to 2000 MHz. The standard is approved, but no manufacturers have launched 25GBASE-T or 40GBASE-T active equipment. This cable is being developed more for data centres.
CAT 6A Application
Enterprise Wireless – Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi6/6E and Beyond Deployments

TIA released TSB-162-A Telecommunications Cabling Guidelines for Wireless Access Points, which recommends Cat 6A cabling for support of WLANs. The cabling infrastructure that forms the backhaul between Wi-Fi access point (AP) and switch must be designed to accommodate current and future standards. To achieve this objective, and support advances in remote powering technology, the recommended cabling design is to install two Category 6A cables per AP to support both current and future wireless technologies.
Multi-Gig / 10G to the Workstation/Desktop

Today media-rich applications are bandwidth-hungry. Further with data migrating to the cloud, the need for faster data transfer has increased, and thus acceptance of 10GbE connections for higher speed is more. This high-speed 10GbE wired networking standard offers ten times the performance of Gigabit Ethernet (1GbE). However, Cat-6A assures Multi-Gigabit (NBASE-T) operation, compared to Category 5e and 6.
Power Over Ethernet (PoE)

The need for higher Wattage capabilities of PoE is increasing due to more intelligent & more power-hungry PoE endpoints. Examples of PoE devices consuming 60W or more include point-of-sale (POS) systems, digital signage, PoE thin clients, intelligent lighting and building management systems. The latest 802.3bt PoE specifications support 60W (Type 3) to 100W (Type 4) of output per cable run. That is as much as three times the maximum Wattage specified in the 802.3at (PoE+) standard.
Even though 802.3bt utilizes all 4 pair of wires, more power output translates into more heat on the wire. When cables get hot, they become susceptible to insertion loss. Transmitting added power to end devices also causes an increased chance of DC resistance unbalance. Such problems are more likely to occur when running on Category 6 cable as compared to Category 6A. Cat-6A conductors are thicker – which help dissipate the heat & take advantage of the high-power PoE without any performance degradation.
Video Surveillance

Next-generation video surveillance cameras that operate at 4K and 8K resolutions and include features such as pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) not only demand higher-power PoE capabilities – but also transmit speeds more than 1Gbp. They stream multiple ultra-high-quality video footages to a network video recorder (NVR) or VMS and perform many video analytics functionalities in a real-time. Cat 6A is designed to support modern day surveillance needs.
Backbone Cabling
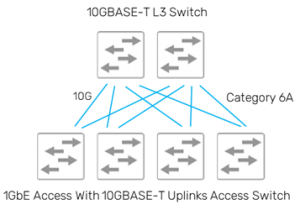
Whenever laying fibre backbone between access Switch & aggregate Switch, it is wise to run Category 6A and utilize 10GBASE-T Ethernet to avoid any bottlenecks on switch uplinks.
Data Centre
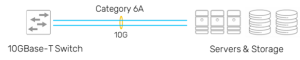
Data Centres require highest level of performance and reliability. Category 6A is the dominant and minimum category copper cabling that is required for the data centres applications today. It supports 10Gb/s applications over Cat 6A twisted pair copper. While addressing the high bandwidth requirement, it can provide fast & easy integration, interconnection & interoperability and reduce the cost of 10GBase-T channels by at least 30% compared to SFP+ channels.
Structured cabling typically represents only about 8~10% of the overall network infrastructure budget. It is also the one of the most disregarded network investments. The cable installed today, will probably not be upgraded, or replaced for next 15-20 years. But the network equipment will most likely be replaced in five to seven years. This is exactly why the cabling installed today should be able to support at least two or maybe three generations of active equipment’s. So, whether it is a new installation or migrating an existing installation, it is recommended to use category 6A cabling infrastructure to support – PoE, IoT, Smart Buildings, Wi-Fi 6 and 10GbE applications in future. Category 6A will serve well for many years to come, and eventually reduce long-term replacement and manpower costs. Category 6A is now the cable of choice and the de facto standard for future-proofing cabling infrastructures.




